All Power Apps Math & Statistical Functions (With Examples)

Math and statistical functions are among the most used functions in Power Apps. Fortunately, they are also some of the easiest functions to learn. Doing math inside of Power Apps has a lot in common with Microsoft Excel. Many of the core functions like SUM and COUNT are exactly the same. In this article I will list all the Power Apps math & statistical functions and show examples of how to use them.
Math Functions
Abs Function
Purpose
Gets the absolute value of a number (without signs). A negative number becomes positive. Positive numbers remain positive.
Syntax
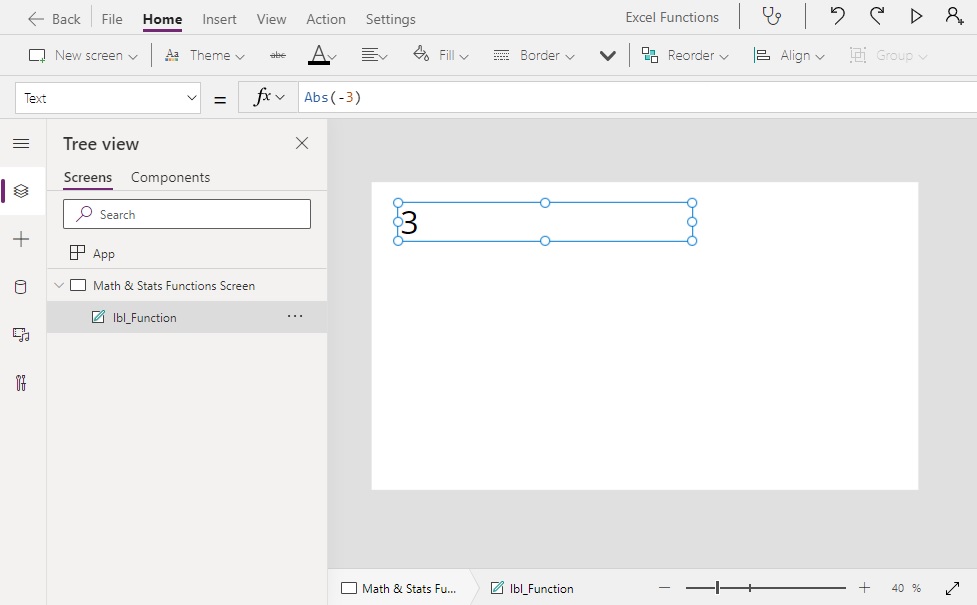
Abs(number)
Arguments
number – a number value to remove signs from
Example
Abs(-3) // Result: 3
Abs(5) // Result: 5
Abs(0) // Result: 0Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Mod Function
Purpose
Returns the remainder of a number divided by another number
Syntax
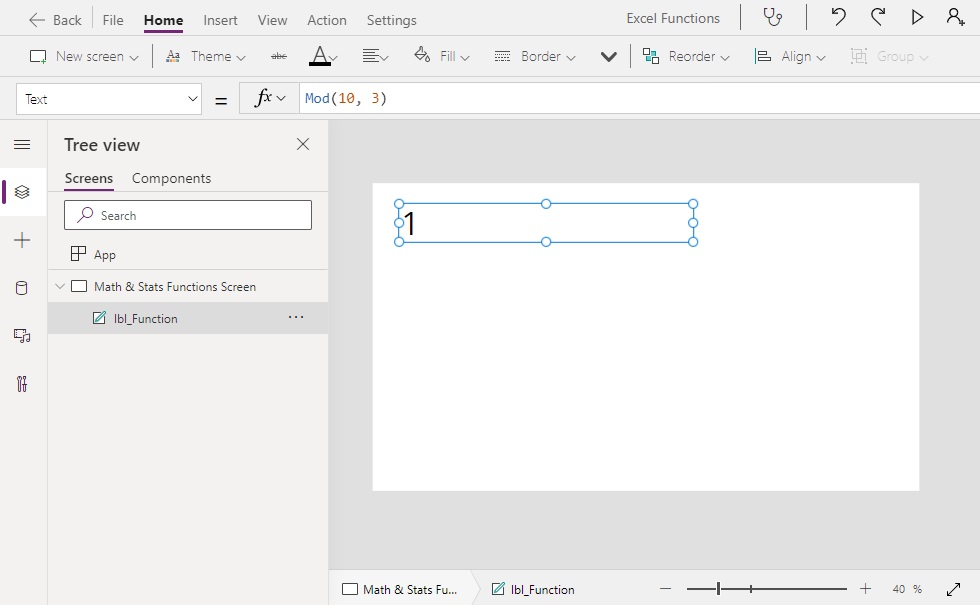
Mod(number, divisor)
Arguments
number – a number value to divide.
divisor– a number to divide another number with.
Example
Mod(10, 3) // Result: 1
Mod(10, 7) // Result: 3
Mod(10, 5) // Result: 0Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Pi Function
Purpose
Returns the mathematical constant Pi (π)
Syntax
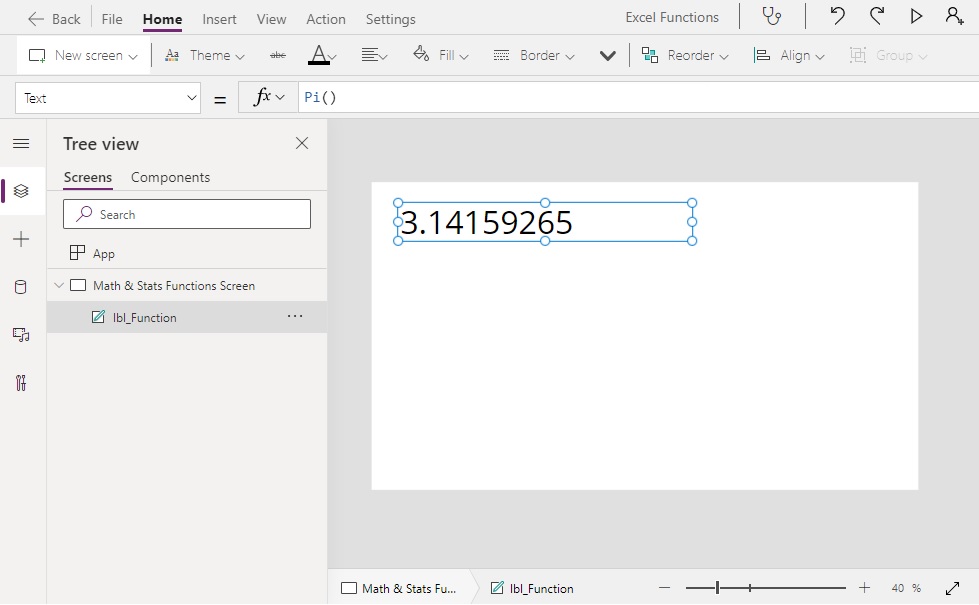
Pi()
Example
Pi() // Result: 3.14159265359Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Power Function
Purpose
Raises a number to the power of another number
Syntax
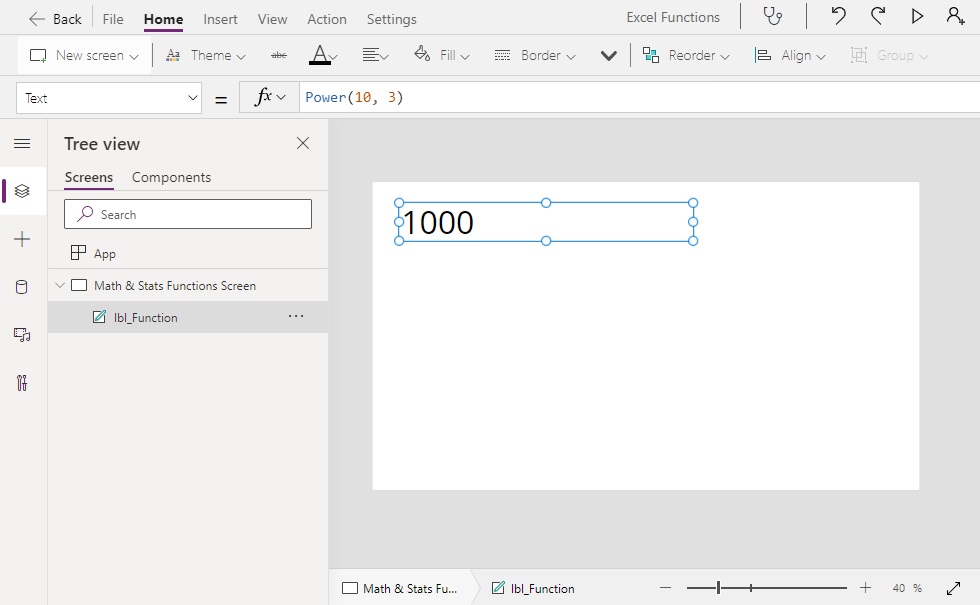
Power(base, exponent)
Arguments
base – the base number to raise
exponent – the exponent to raise a base number by
Example
Power(10, 2) // Result: 100
Power(10, 3) // Result: 1000
Power(5, 3) // Result: 125Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Sqrt Function
Purpose
Get the square root of a number.
Syntax
Sqrt(number)
Arguments
number – a number value to get the square root of
Example
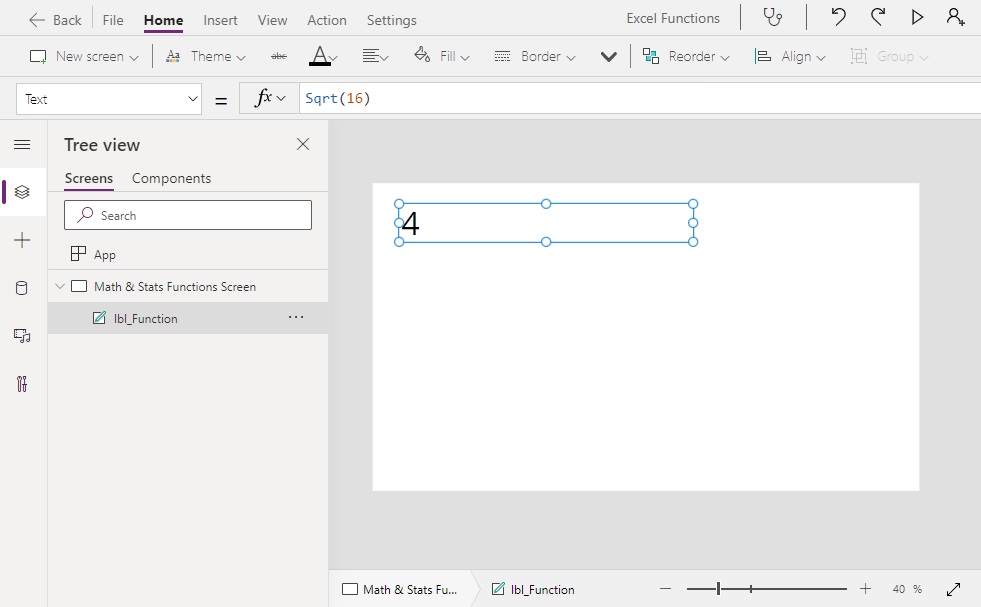
Sqrt(4) // Result: 2
Sqrt(16) // Result: 4
Sqrt(1) // Result: 1Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Sum Function
Purpose
Calculates the sum for a table of numbers
Syntax
Sum(source, expression)
Arguments
source – a table of numbers to be added
expression – a formula evaluated for each row of table that provides a set of numbers to be added together
Example
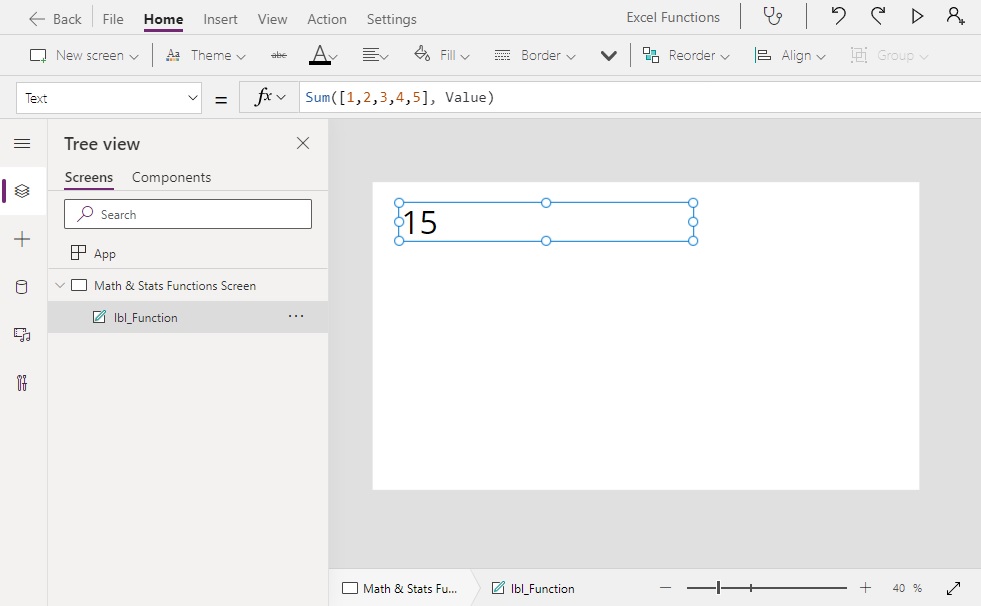
Sum([1,2,3,4,5], Value) // Result: 15
Sum(
Table(
{Letter: "A", Value: 1},
{Letter: "B", Value: 2},
{Letter: "C", Value: 3},
{Letter: "D", Value: 4},
{Letter: "E", Value: 5}
),
Value
)
// Result: 15Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Statistical Functions
Average Function
Purpose
Calculates the average (arithmetic mean) for a table of numbers
Syntax
Average(source, expression)
Arguments
source – a table of numbers to get the average from
expression – a formula evaluated for each row of table that provides a set of numbers to be averaged
Example
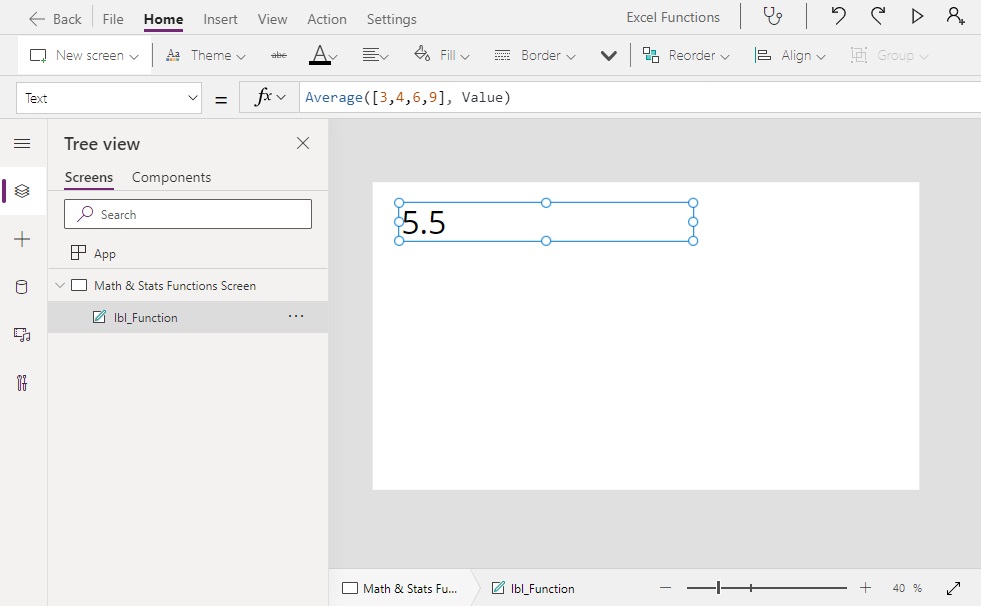
Average([1,2,3,4,5], Value) // Result: 3
Average([3,4,6,9], Value) // Result: 5.5Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Count Function
Purpose
Counts the number values in a single column table
Syntax
Count(source, expression)
Arguments
source – a single-column table of numbers to count
expression – a logical expression that decides which numbers to include in the count
Example
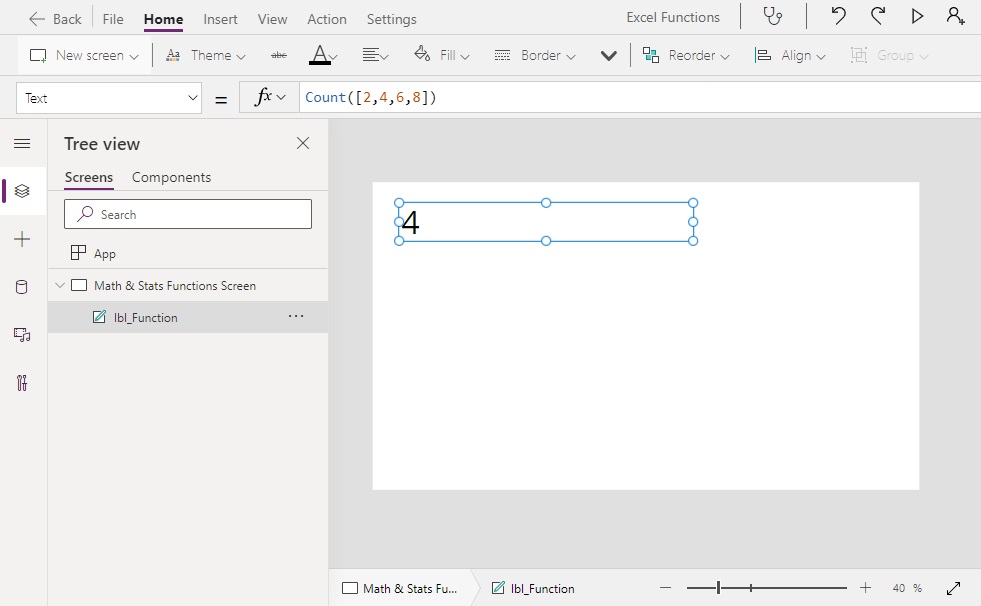
Count([2,4,6]) // Result: 3
Count([2,4,6,8]) // Result: 4
Count([2,4,6,8,Blank()]) // Result: 4Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
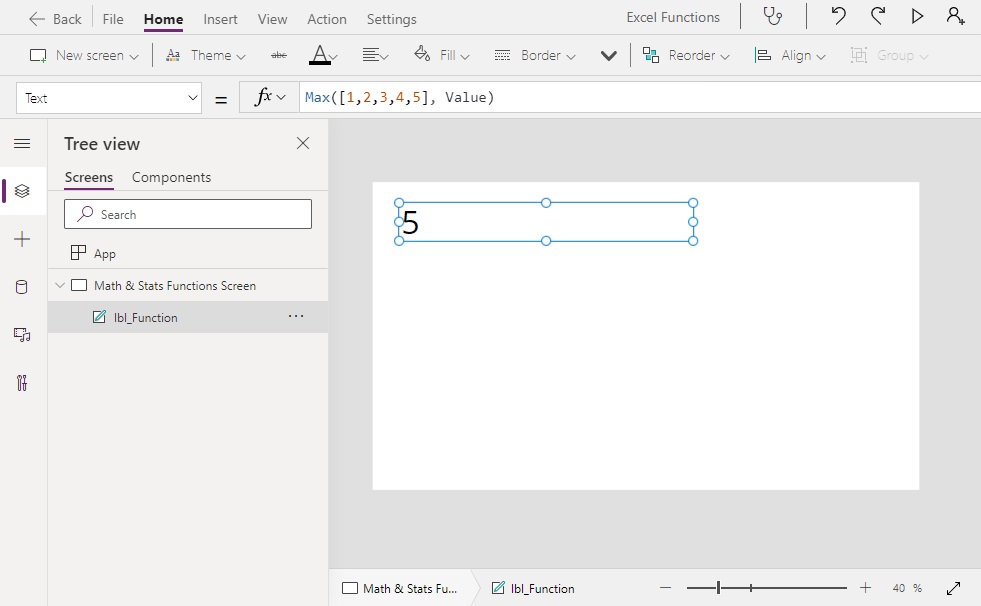
Max Function
Purpose
Returns the maximum value from a table of numbers
Syntax
Max(source, expression)
Arguments
source – a table of numbers to get the maximum from
expression – a formula evaluated for each row of table that provides a set of numbers for the maximum value calculation
Example
Average([1,2,3,4,5], Value) // Result: 5
Average([-2-1,0,1,2], Value) // Result: 2Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
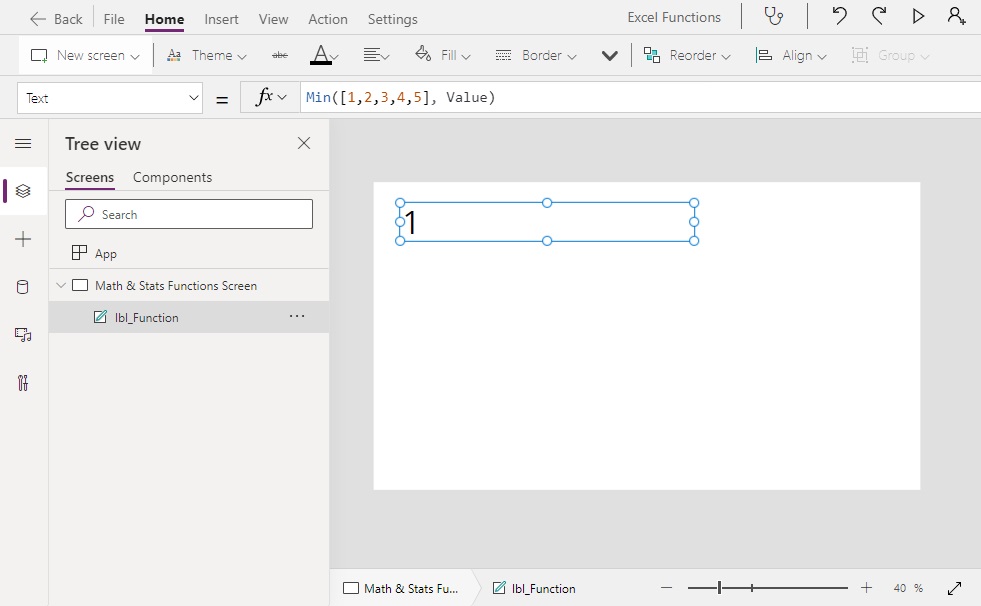
Min Function
Purpose
Returns the minimum value from a table of numbers
Syntax
Min(source, expression)
Arguments
source – a table of numbers to get the minimum from
expression – a formula evaluated for each row of table that provides a set of numbers for the minimum value calculation
Example
Min([1,2,3,4,5], Value) // Result: 1
Min([-2-1,0,1,2], Value) // Result: -2Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
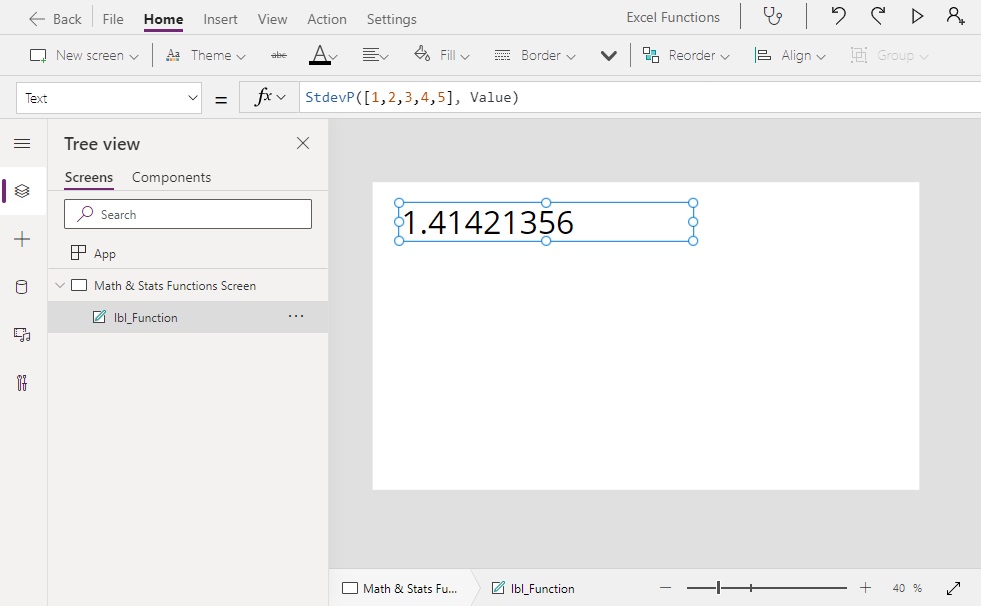
StdevP Function
Purpose
Calculates the standard deviation for a table of numbers
Syntax
StdevP(source, expression)
Arguments
source – a table of numbers to get the standard deviation from
expression – a formula evaluated for each row of table that provides a set of numbers for the standard deviation calculation
Example
StdevP([1,2,3,4,5], Value) // Result: 1.41421356
StdevP([1,3,7,11], Value) // Result: 3.84057287Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
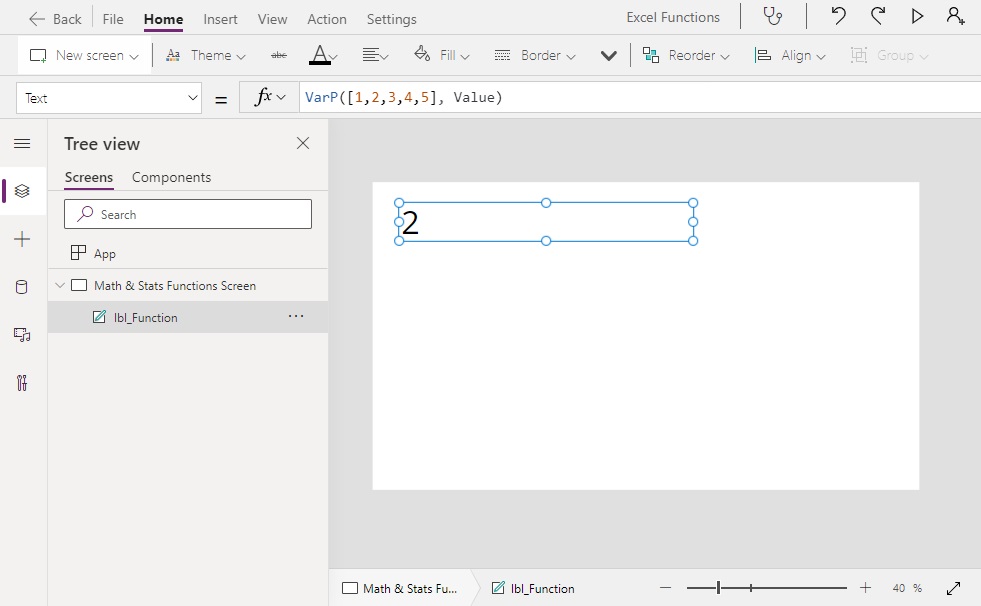
VarP Function
Purpose
Calculates the variance for a table of numbers
Syntax
VarP(source, expression)
Arguments
source – a table of numbers to get the variance
expression – a formula evaluated for each row of table that provides a set of numbers for the variance calculation
Example
VarP([1,2,3,4,5], Value) // Result: 3.84057287
VarP([1,3,7,11], Value) // Result: 14.75Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Rounding Functions
Round Function
Purpose
Rounds a number to the nearest number with the chosen number of digits
Syntax
Round(number, num_digits)
Arguments
number – a number to round
num_digits – the number of decimal places in the rounded number
Example
Round(3.2, 0) // Result: 3
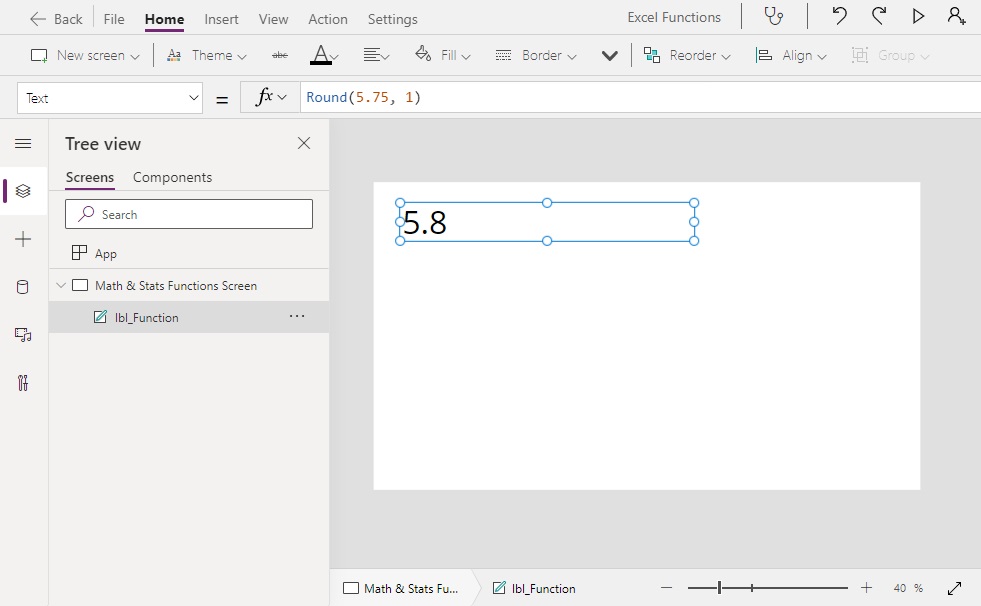
Round(5.75, 1) // Result: 5.8
Round(1.355, 2) // Result: 1.36Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
RoundUp Function
Purpose
Rounds a number up to the next number with the chosen number of digits
Syntax
RoundUp(number, num_digits)
Arguments
number – a number to round up
num_digits – the number of decimal places in the rounded number
Example
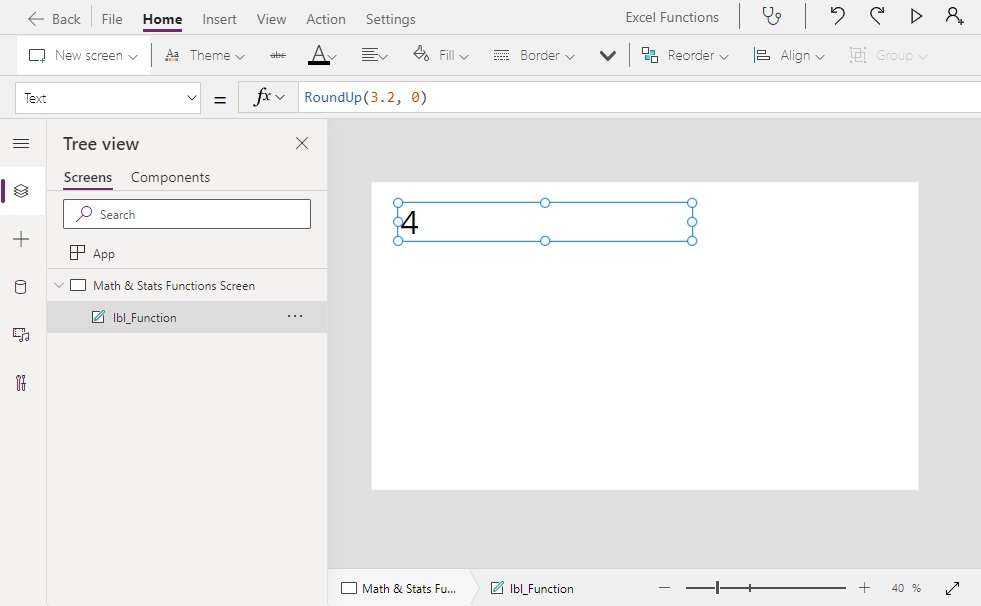
RoundUp(3.2, 0) // Result: 4
RoundUp(5.75, 1) // Result: 5.8
RoundUp(1.355, 2) // Result: 1.36Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
RoundDown Function
Purpose
Rounds a number down to the next number with the chosen number of digits
Syntax
RoundDown(number, num_digits)
Arguments
number – a number to round down
num_digits – the number of decimal places in the rounded number
Example
RoundDown(3.2, 0) // Result: 3
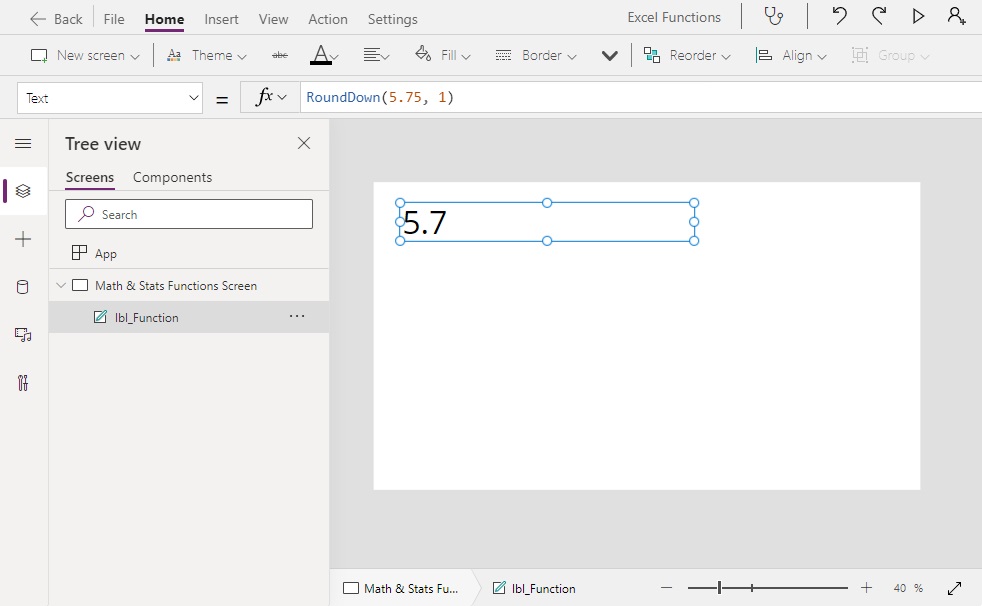
RoundDown(5.75, 1) // Result: 5.7
RoundDown(1.355, 2) // Result: 1.35Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Int Function
Purpose
Rounds a decimal number or a text value to the nearest integer (a number with no decimals)
Syntax
Int(number)
Arguments
number – a number to change into an integer
Example
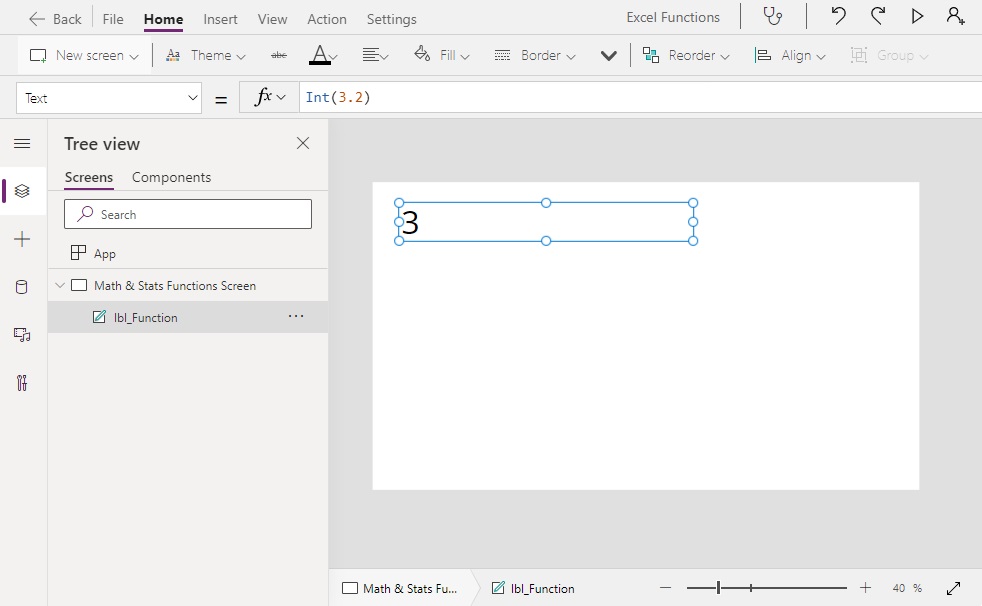
Int(3.2) // Result: 3
Int(5.75) // Result: 6
Int("1") // Result: 1Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Trunc Function
Purpose
Removes the decimals from a number
Syntax
Trunc(number)
Arguments
number – a number to truncate
Example
Trunc(3.2) // Result: 3
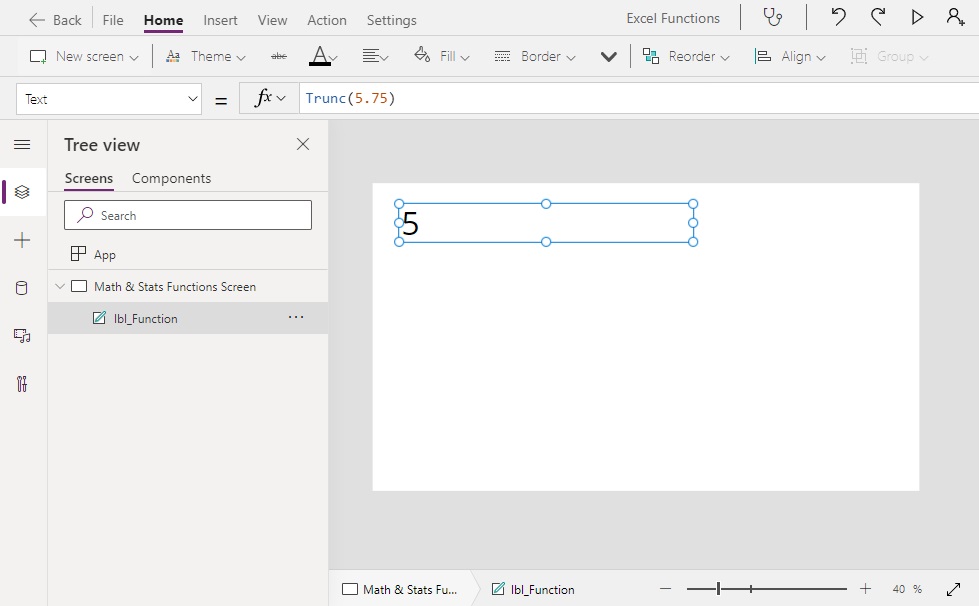
Trunc(5.75) // Result: 5
Trunc(1) // Result: 1Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Count Functions
CountA Function
Purpose
Counts the number and text values in a single column table. An empty string “” counts as a non-blank value
Syntax
CountA(number, num_digits)
Arguments
source – a single-column table of numbers or text to count
expression – a logical expression that decides which numbers to include in the count
Example
CountA([2,4,6]) // Result: 3
CountA(["A","B","C","D"]) // Result: 4
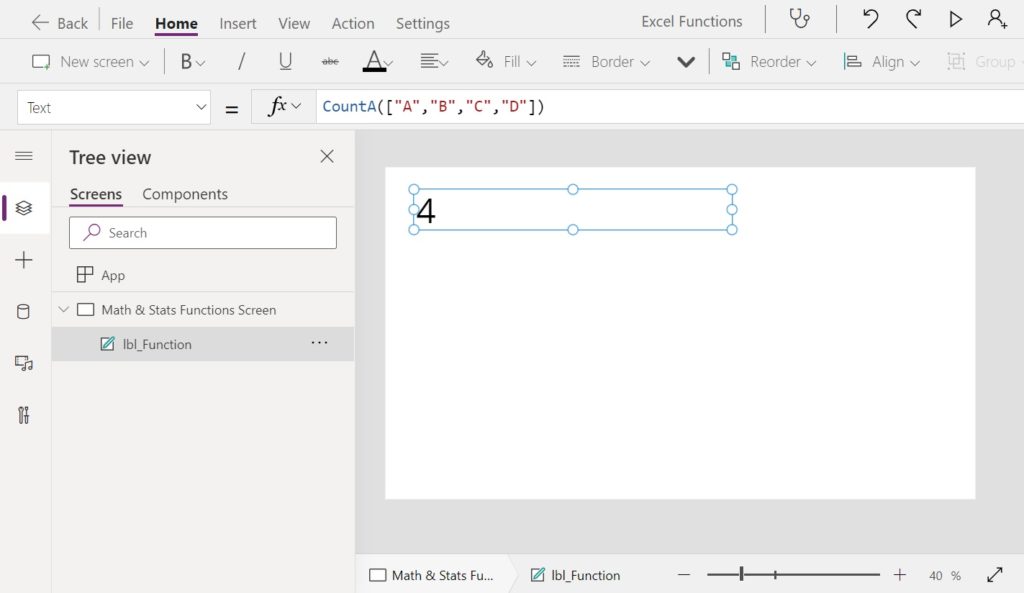
CountA(["A","B","C","D",""]) // Result: 5Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
CountIf Function
Purpose
Counts the number of rows in a table which meet a set of conditions
Syntax
CountIf(source, condition1 [, condition2, …])
Arguments
source – a table of values to count
condition – a logical expression evaluated for each row of the table that decides which rows to count
Example
CountIf(["A","B","A","A","B"], Value="A") // Result: 3
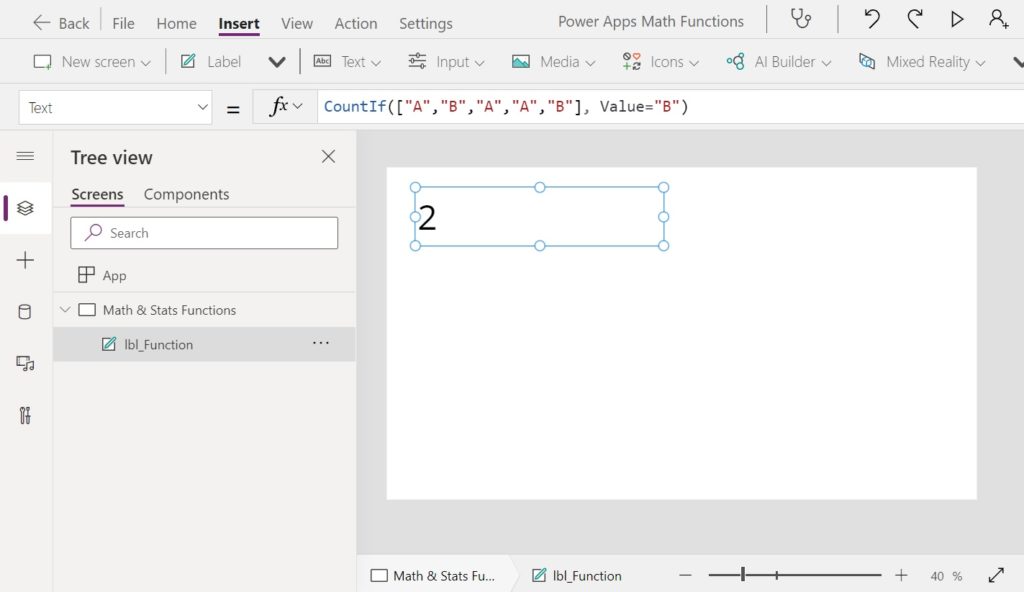
CountIf(["A","B","A","A","B"], Value="B") // Result: 2
CountIf(
Table(
{Test:"English", Score: 90},
{Test:"English", Score: 55},
{Test:"Math", Score: 73},
{Test:"Math", Score: 85}
),
Score>=65
)
// Result: 3Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
CountRows Function
Purpose
Counts the number of rows in a table
Syntax
CountRows(source)
Arguments
source – a table whose rows will be counted
Example
CountRows(
Table(
{Value: "A"},
{Value: "B"},
{Value: "C"}
)
)
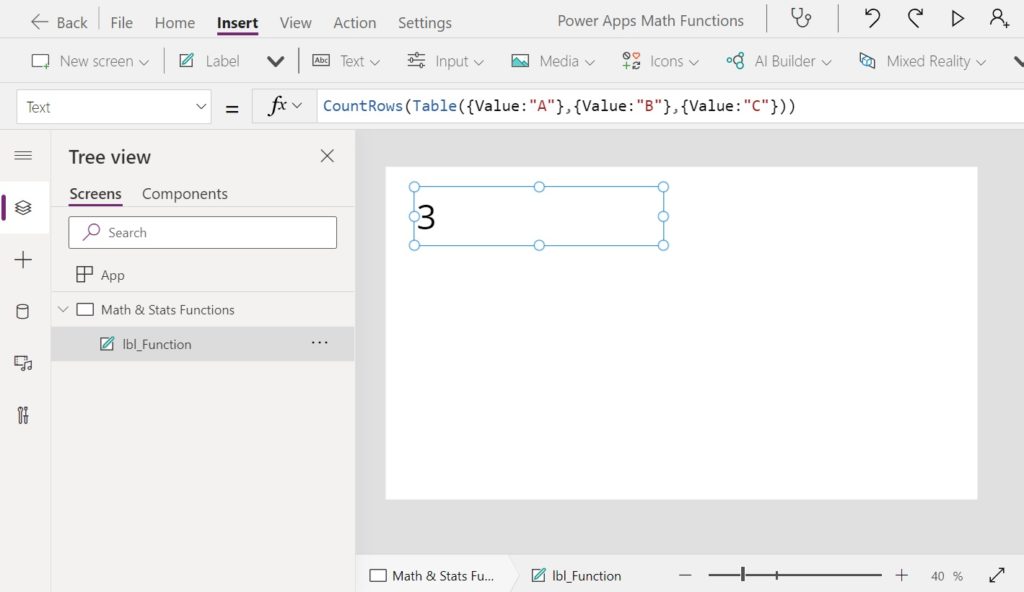
// Result: 3Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Random Functions
Rand Function
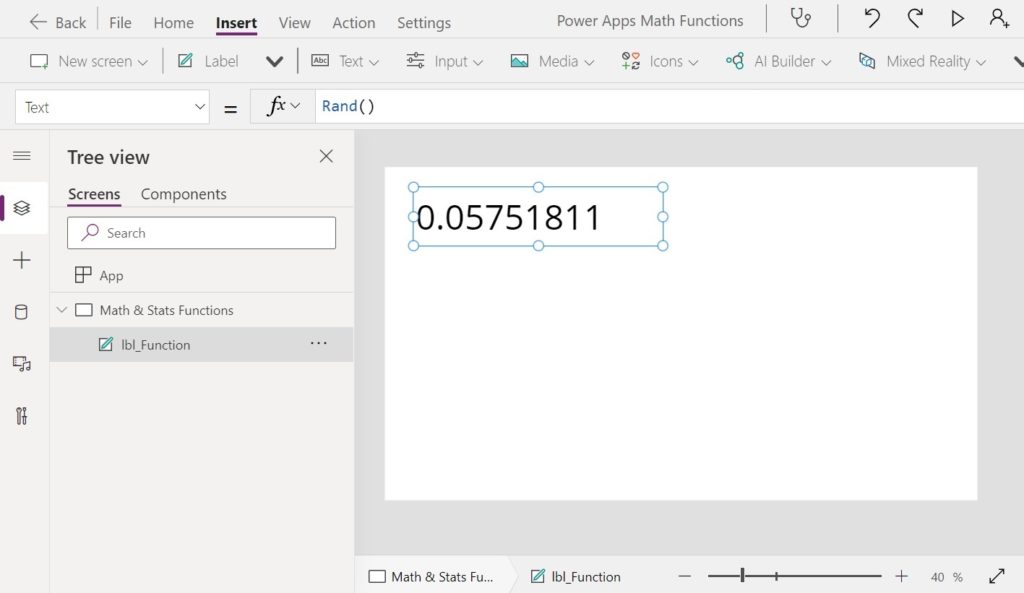
Purpose
Generates a psuedo-random decimal number between 0 and 1
Syntax
Rand()
Example
// Result: 0.18009472
// Result: 0.25365866
// Result: 0.52303658Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)
RandBetween Function
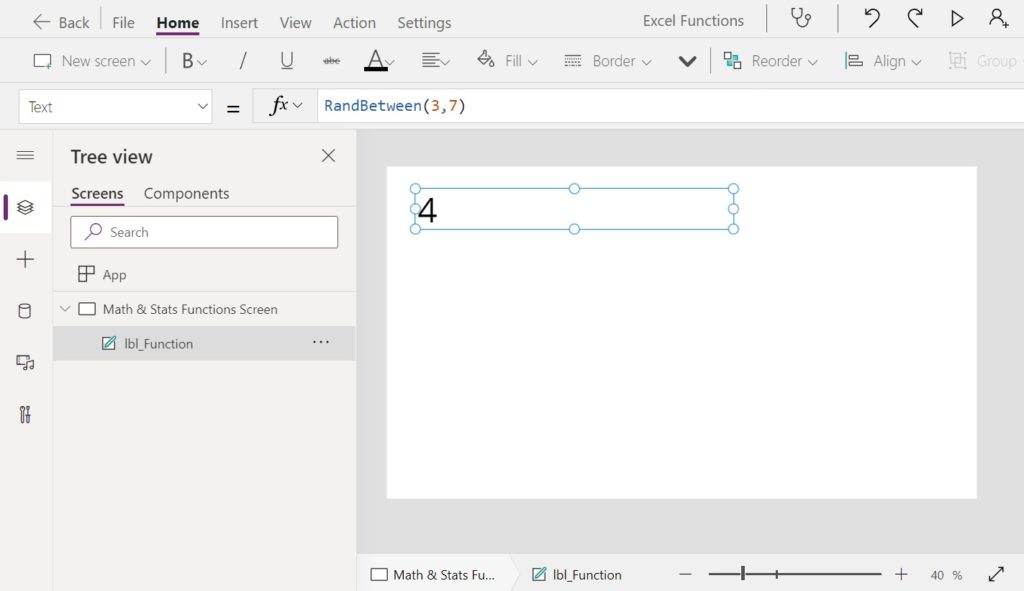
Purpose
Generates a random number within a range
Syntax
RandBetween(bottom, top)
Syntax
bottom – the lowest random number in the range
top – the greatest random number in the range
Example
// RandBetween(3, 7) // Result: 4
// RandBetween(3, 7) // Result: 3
// RandBetween(3, 7) // Result: 6Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)
Logarithm Functions
Exp Function
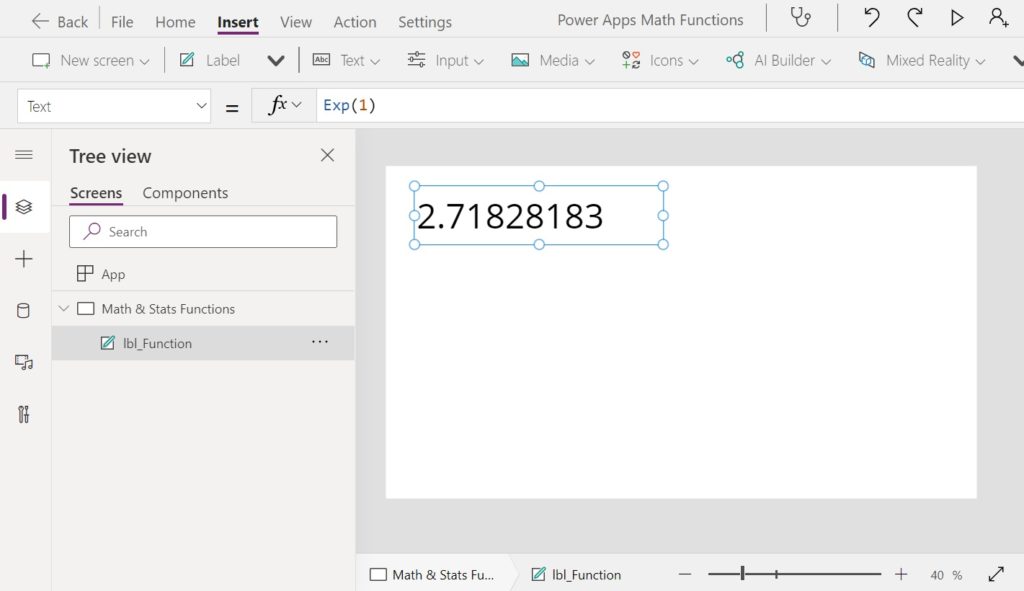
Purpose
Returns e to the power of a given number. The mathematical constant e (also known as Euler’s number) is equal to 2.71828182845904, the base of the natural logarithm.
Syntax
Exp(number)
Arguments
number – the number e is raised to the power of
Example
Exp(1) // Result: 2.71828182845
Exp(2) // Result: 7.38905609893Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Ln Function
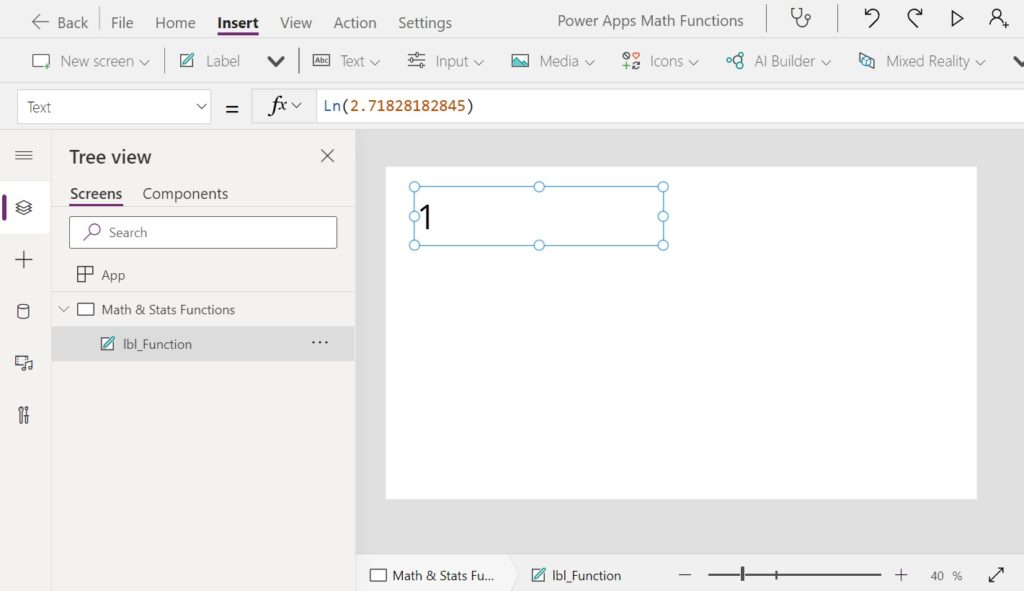
Purpose
Returns the natural logarithm of a number – the logarithm to the base of the number e (Euler’s number)
Syntax
Ln(number)
Arguments
number – the number to find the natural logarithm of
Example
Ln(2.71828182845) // Result: 1
Ln(7.38905609893) // Result: 2 Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
Log Function
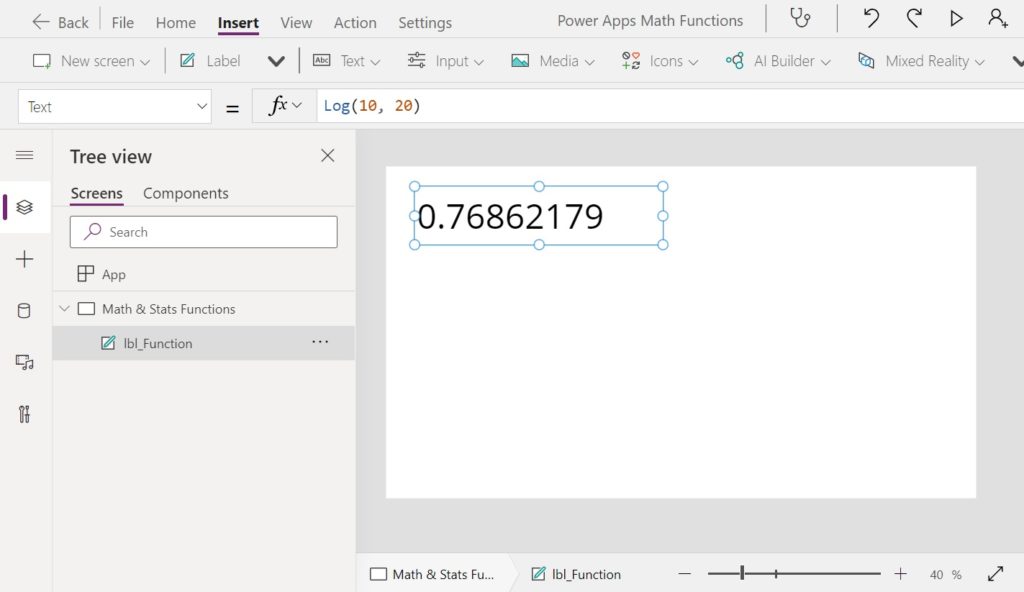
Purpose
Calculates the logarithm of a number for a given base
Syntax
Log(number, base)
Arguments
number – the number to calculate the logarithm for
base – the base of the logarithim
Example
Log(10, 10) // Result: 1
Log(10, 15) // Result: 0.85027415
Log(10, 20) // Result: 0.76862179 Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Did You Enjoy This Article? 😺
Subscribe to get new Copilot Studio articles sent to your inbox each week for FREE
Questions?
If you have any questions or feedback about All Power Apps Math & Statistical Functions (With Examples) please leave a message in the comments section below. You can post using your email address and are not required to create an account to join the discussion.






Thank you!